The rise of AI tools like ChatGPT and Midjourney has opened a floodgate of possibilities for creators. Whether it's writing blog posts, designing logos, or drafting client emails, AI-generated content is already powering online businesses across platforms like Medium, Etsy, Substack, and Upwork. But if you're using tools like GPT to generate content for profit, you might be asking: "What am I actually allowed to do with this content? And what could land me in legal trouble?"
This guide will help creators navigate the gray zone between innovation and infringement. It's meant for curious builders who want to earn from AI tools in a grounded and future-ready way. Every claim is supported by references to official guidance or recent legal developments.
1. Who Owns AI-Generated Content?
U.S. law requires human authorship before copyright can be granted. Works created entirely by AI are ineligible under current standards. The U.S. Copyright Office has stated that prompts alone are not enough. Human involvement must extend to expressive editing, arrangement, or creative selection in order to qualify for protection [1], [2].

Federal court decisions have reinforced this stance. In the case Thaler v. Perlmutter, an artwork entirely generated by a machine had its copyright claim denied because it lacked human authorship [3], [4].
2. Proving Human Creativity in Practice
Curious creators often ask: What counts as meaningful human input? Here are practical ways to strengthen authorship claims:
-
Use iterative prompting, editing, and blending outputs with human-written sections.
-
Document your process. Saving prompt history, timestamps, or screen recordings can help demonstrate creative control.
-
Focus on selection and arrangement. Curating drafts into a coherent narrative or design shows originality [2], [6].
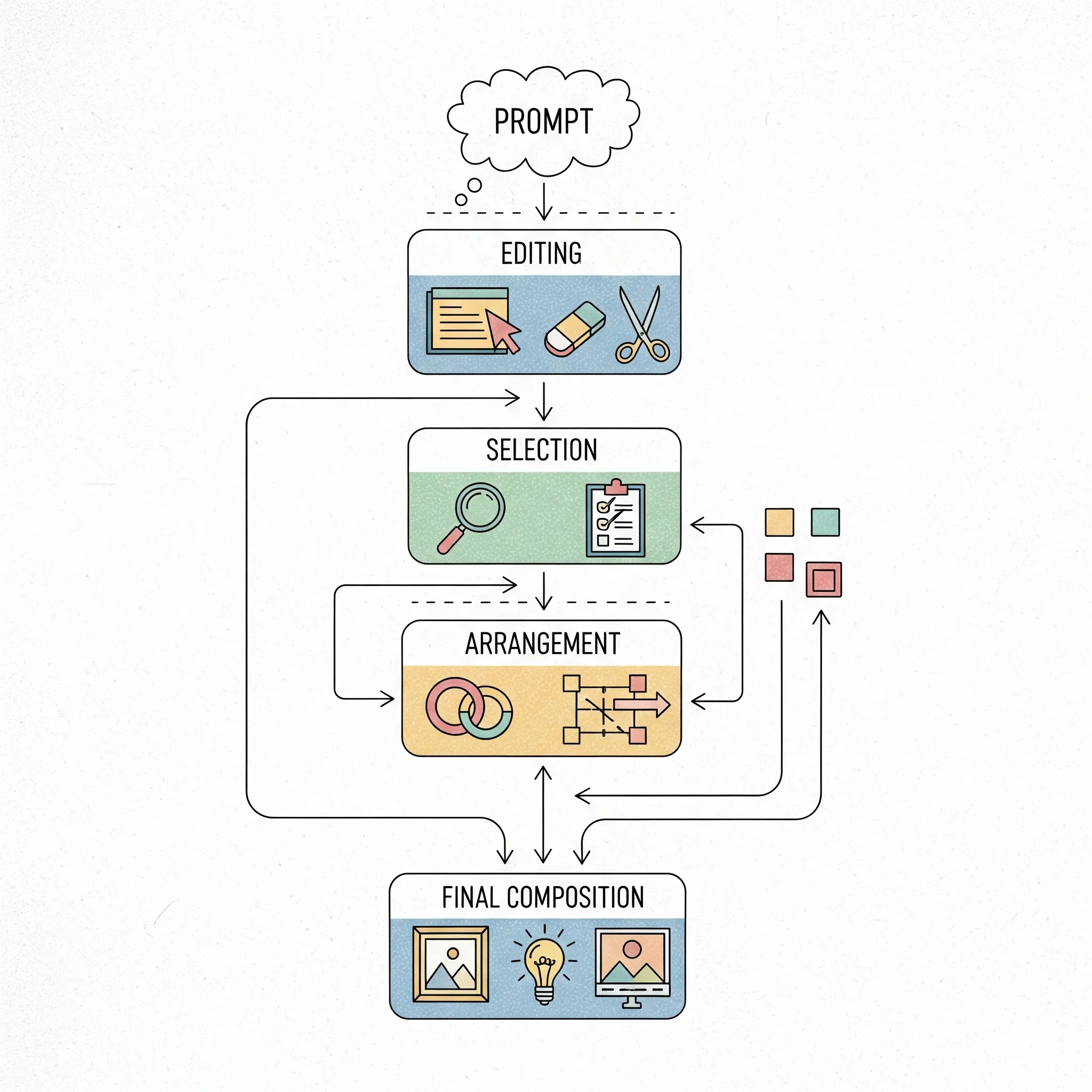
These methods together form a defensible narrative if your registration is ever scrutinized.
3. Monetizing Without Copyright
You don't need copyright to sell AI-generated content. You only need:
-
A clear commercial license from the platform (for example, OpenAI or Midjourney). Many providers allow monetization if you subscribe or follow their terms [1].
-
Compliance with each platform you publish on. Some platforms require AI disclosure or proof of rights.
-
Transparent communication with your audience. Disclosure often builds trust rather than harming credibility.
4. Risks and Liability: Similar Outputs and Infringement
Duplicate or nearly identical content can arise from similar prompts. Research indicates models can replicate verbatim passages from their training data and generate duplicate images even from benign prompts [5], [7].

If two creators run the same prompt, they may receive similar outputs. That raises questions about originality and risk management.
To reduce that risk:
-
Use layered prompt engineering techniques, such as chain-of-thought or task instruction prompting, which reduce similarity to training data [8].
-
Always refine or customize generative output before publishing.
5. Creators Ask: What If Two People Use the Same Prompt?
This scenario often comes up. Generative models are probabilistic and can output similar results for common prompts. Duplicate outputs are not illegal by themselves. But if one creator claims copyright or pursues action, having documentation of your process and your distinct edits helps. The logic is that authorship is about transformation rather than copying.
If someone sues claiming similarity to their work, courts examine whether your output was substantially similar to a protected work. Copying common language or generic visuals is less risky than near-replication of unique content.
6. Protecting AI-Generated Work Without Copyright
Even when copyright is unavailable, creators can still protect their business with other intellectual property tools:
-
Trademark applies to names, taglines, logos, or trade dress that sets your brand identity apart.
-
Trade dress law can cover distinctive visual design or product structure if it signals origin or quality [2].

These tools help secure brand value even if individual outputs lack traditional copyright.
7. How to Make AI-Assisted Work Original and Stand Out
Generative AI is easily copyable. To build a defensible and unique creator business:
-
Blend AI outputs with personal expertise, voice, or curated context.
-
Add value beyond generation: commentary, interviews, charts, links, or original structuring.
-
Offer unique formats or niches, such as prompt templates, educational toolkits, or consulting services.
These approaches are harder to replicate and lean into your experience or point of view.
8. Beyond Content: Designing Durable AI-Based Offerings
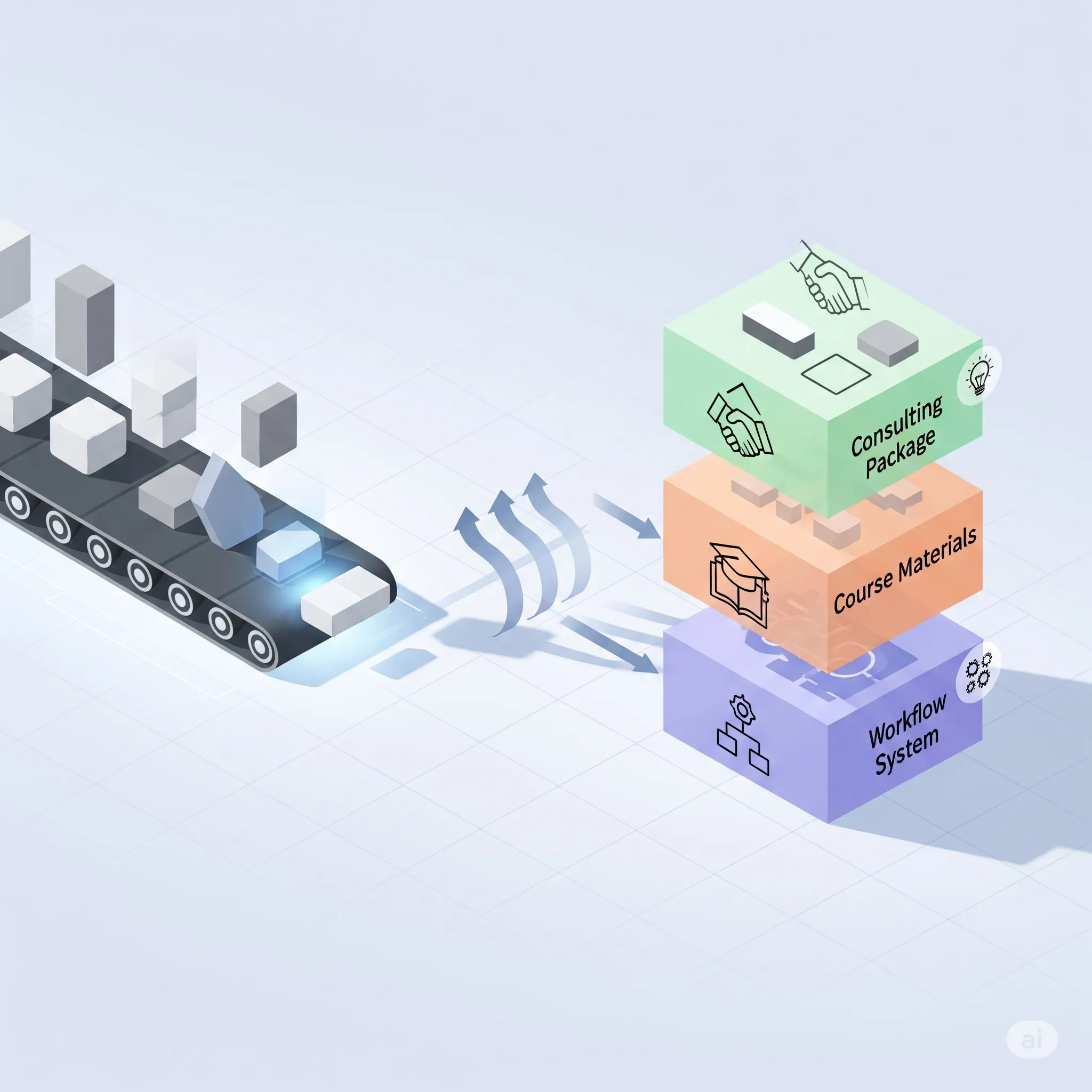
Instead of treating AI as a content factory, think of it as a tool for building systems and services:
-
Sell prompt libraries or workflow templates instead of one-off generated outputs.
-
Offer courses or coaching that teach others how to deploy AI responsibly.
-
Provide consulting on AI strategy, compliance, or prompt engineering workflows rather than generic content.
This moves you from content to consulting, increasing business defensibility and earnings potential.
9. Ethics and Community Standards in AI Creation
Even when disclosure is not legally required, there are growing community norms around transparency and ethics:
-
Be open about using AI in your process. Readers may feel more trusting if they know where tools are involved.
-
Respect fair use. Avoid prompts that replicate protected styles or mimic well-known creative content.
-
Learn from emerging debates. Many creators are forming informal ethical codes around attribution, reuse, and compensation.
Transparency, ethical intent, and thoughtful design help build credibility and sustainability.
10. Summary Takeaways
-
Copyright requires discernible human input, which means just typing a prompt in isolation is not enough for protection [2], [4], [6].
-
Create valuable work not by raw AI output but by editing, curating, and contextualizing.
-
Commercial licensing and compliance matter more than ownership if you only plan to monetize.
-
Use trademarks or trade dress to protect brand elements that outlast individual pieces.
-
To differentiate and avoid duplication issues, leverage layered prompts, custom edits, and workflow transformation strategies.
-
Build business models centered on services, education, or systems, not just generated content.
References
-
U.S. Copyright Office. Copyright Registration Guidance for Works Containing AI-Generated Material (Part 2), January 2025.
-
U.S. Copyright Office. Copyright and Artificial Intelligence: Policy and Practice Overview, 2024.
-
Skadden, Arps. Commentary on Thaler v. Perlmutter, D.C. Circuit Decision, 2025.
-
Perkins Coie. Summary of Human Authorship Rulings, 2025.
-
IEEE Spectrum. Plagiarism and Duplication in AI Outputs: A Technical Analysis, 2024.
-
Perkins Coie. Creative Modification and the Human Authorship Requirement, 2024.
-
Norton Rose Fulbright. AI and IP Infringement Risk: Guidance for Creators, May 2025.
-
arXiv.org. Prompt Engineering Techniques for Reducing IP Overlap in Generative AI, May 2025.